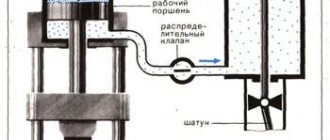
Well, how much we love wild abstruse definitions: special heating devices for the purpose of increasing the plastic characteristics of the metal. Let's try to translate all this disgrace into human language.
A forge is essentially a stove. It is clear that it has its own characteristics, varieties and technological nuances, but it is still a stove. It is needed to heat metal parts to a temperature so that they can be forged, that is, subjected to deformation.
This is the main and general fact for all kinds of forges - from primitive country crafts on bricks to industrial furnaces with many technological features of application and purpose.
Heating the workpiece in a forge
A forge furnace requires two main and only properties: it can produce very high temperatures, up to 1200 - 1500°C, and the ability to maintain the desired temperature for a certain time. In other words, we need strong and even heat.
At what temperature do metals become forgeable, that is, begin to be ductile? This is different for all metals and alloys. But the visual sign that the metal part has heated up to the required temperature is also common - this is the orange color of the part.
All metals respond to heat by changing color from dark red to piercing white. So the orange color is a signal that you can start real blacksmithing work on metal.
Drawing of a blacksmith's forge.
The only metal that behaves quite meanly and does not change its color when heated is aluminum. It is not the easiest metal to forge and weld in principle; with aluminum you need to know and apply many special requirements.
So, the absence of an orange color while it has already warmed up for forging is a significant factor that makes it difficult to work with this capricious metal and its alloys. After all, you can’t overheat. Underheating is also no good.
Classification of forges
There are several criteria by which you can classify all these stoves into neat types.
Most often, forges are divided according to the type of fuel on which they operate:
Solid fuel forges
They run on coal. Their use is becoming less and less common, since coal is a fuel that does not provide a stable and even fire, which is the most important requirement for a forge. Not only that, such stoves require not just coal, but high-quality coking wood coal or hard coal of the same quality.
There are lovers of such exotic things, so below we will focus on a couple of tips for arranging such a stove.
Gas forges
We will talk about this type of stove in detail: they are the most common in both home handicraft workshops and professionally equipped forging centers. The gas forge is, without a doubt, the favorite tool of domestic blacksmiths.
Liquid
Here the main type of fuel is fuel oil.
Coal forge forge.
According to the design decision, forges are divided into closed and open. In size they come in small, medium and large. That, in fact, is the entire classification of forges. A homemade forge for forging is a very real thing and, most importantly, necessary on the farm.
The main thing is to decide which kind of forge suits you. And to do this, you must clearly know what kind of forging products you are going to make, for whom and in what quantity.
Basic design of a homemade forge
The first question is: what kind of forge should I make - open or closed? The answer will depend on your plans - what are you going to do in your blacksmith shop? If this is a hobby in the form of artistic forging in small quantities exclusively for the home and gifts for relatives, then it will be quite enough for you to acquire an open forge.
It is much simpler and will cost you less in terms of money and labor costs. An open forge makes it easier to heat massive or long parts.
If you plan to work with metals seriously, for example, to earn money, then we would advise you to build a closed forge with your own hands.
These are the parts that make up a well-assembled forge:
- frame on racks for support, everything must be made of steel;
- under – bottom or lower part of the wall of the hearth;
- slide-type damper with special holes to accelerate metal heating and save fuel;
- fan;
- smoke exhaust pipe
- linings – thermal protection of the stove in the form of fireclay bricks;
- recuperator - a special device for returning the generated heat in the form of furnace gases and, thus, efficient use of resources.
Rules for safe operation of equipment
If used incorrectly, gas cylinder equipment can become a source of a strong explosion or fire.
When performing welding work, you should definitely use personal protective equipment: glasses, gloves, special shoes.
Before starting work, you need to thoroughly inspect the equipment for damage. If the equipment gets dirty, be sure to remove the dirt
You can work with propane cylinders only in well-ventilated areas, and the air temperature should not be below 0 °C.
Absolutely forbidden:
- Work near open flames.
- Keep the cylinder tilted when working.
- Place the vessels in the sun.
- Carry out work without a gearbox.
- Heat the gearbox over an open fire.
In addition, if you smell gas, you must immediately stop working and turn off the valve on the cylinder. We also recommend that you familiarize yourself with the main reasons for the explosion of gas cylinders.
When working without personal protective equipment, you can get burned, not only from an open flame, but also from accidentally touching hot parts.
If the considered homemade burners are not suitable for you, we recommend that you familiarize yourself with other options for making useful homemade products discussed in our articles - a burner made from a blowtorch and a burner for a sauna stove.
Building a solid fuel forge
The main disadvantage of solid fuel forges is that coal itself cannot produce the required temperature above 1000°C. Therefore, such stoves always require an air stream. Previously, these were bellows, now more often the air is supplied through a pipe with a welded end, also made of steel.
The easiest way is to dig such a stove directly in the ground - just line the hole with fireproof bricks. A homemade forge can be made differently: from a steel plate of decent thickness, build a table with a grate made of cast iron or steel.
Grate for the forge.
The table plate must be made from a blank with a thickness of at least 5 mm. If you install an open design forge outdoors, you will not need to deal with special ventilation.
Here are the main steps for building a homemade coal-fired forge:
- Build a platform for the foundation with concrete and reinforced rods.
- Fold the bricks into a rectangular base; the table surface can be of any height.
- Make a hole in any wall of the base for the blower.
- Assemble the floor from special refractory bricks onto the base.
- Install a grate with holes, which must also be made of fire-resistant material, for which a cast-iron door from an old stove is perfect.
- After installing the grate, add walls made of the same refractory brick.
- Do not forget to leave a hole in one wall for air supply; it is better to do this immediately when laying bricks.
- Install a fan into the air supply pipe.
- If you are making a closed structure, be sure to build a chimney, which is absolutely necessary for draft.
Such a forge can be made mobile - it all depends on you. An old gas stove can serve as an excellent frame for a solid fuel forge.
Building a gas forge
Before you start building a gas forge with your own hands, you need to determine the parameters of the hearth - its area.
There is a clever formula for this:
N=H×F
N is the productivity of the hearth, which depends on the tension H and the hearth area F. It has been calculated that the gas supply speed in the range from 1 to 1.5 m/sec is sufficient to optimally maintain the required temperature in the hearth.
Diagram of a gas burner for a forge.
You know the area of your workshop and the approximate number of forging parts in kilograms that you plan to produce. With this data you derive the hearth tension with a maximum permissible upper limit of 150 kg/m².
Necessary materials you need to get started:
- fire-resistant brick such as dinas or chamotte;
- plates with a thickness of at least 5 mm made of heat-resistant steel;
- steel profile for the racks, frame and valve of the hearth;
- pipe for the chimney and ventilation duct made of steel;
- putty for sealing cracks between bricks with heat-resistant properties;
- sheet metal or an additional layer of refractory bricks for lining on the outside;
- burners from high-power double-circuit boilers;
- fan;
Gas forges can also be open. With it everything is much simpler; it will be enough to install grate bars with air supply for greater heating efficiency. In this case, combustion substances are removed by a fan made of heat-resistant metal.
It is better to place the support frame close to one of the walls of your workshop. The choice of wall must be made taking into account the fact that a chimney and ventilation pipe will be needed, so it is better not to use adjacent walls, if any.
The most important condition is strict compliance with fire safety rules, which consists of using only fire-resistant and heat-resistant materials. It doesn't hurt to check what your workshop walls are made of. We treat various types of plasterboard structures with great caution.
It is better to weld the racks and the frame itself from low-alloy steel according to drawings that can be downloaded on the Internet. Low-alloy steel is strong, lightweight and, most importantly, resistant to specific high-temperature corrosion. The external lining must be thought out in advance so that holes for its fastening are immediately made in the support frame.
Now about refractory bricks and masonry. It is important to buy real certified fireclay bricks made in accordance with GOST 390-79. If you purchase a brick that does not meet the standard, you risk that ordinary bricks will begin to melt at a temperature of 1000°C.
Real fireclay bricks are cream-colored with small pores in small quantities, they are much heavier than ordinary ceramic ones, the weight of one large fireclay brick reaches 5 kg. The most suitable brands of fireclay are ShB, ShA and ShPD.
Construction of a forge.
The second type of refractory bricks is dinas. These bricks are more expensive, but more resistant to high temperatures: they can withstand temperatures of 1800°C. They are lighter than fireclay bricks due to the high proportion of silicon salts in their composition.
If you have the opportunity, it is better to line the forge with silica brick: forges made of refractory silica brick are more durable and can withstand the most severe temperature conditions.
The bricks are laid with a mortar of refractory clay with the addition of chamotte and silica powder in a precise proportion of 60:40. Treat the chimney and fan around the perimeter with metal corners.
The most important final stage is drying the entire structure. After this, you need to check how the fans for the forge work. And only then will it be possible to perform a test run.
Direct stationary burners 1/2″ and 3/4″
This burner, in addition to being intended for stationary use, cannot be operated separately from the stove. When working separately, the flame may go out (it is blown off at a pressure greater than a certain value and the flame jumps inward to the nozzle itself at a pressure less than a certain value). This is explained by the fact that it does not use a flame divider, which ensures stable operation. Instead, there is a small bell, but you can do without it, with a straight pipe. Just be sure to insert the pipe or socket into the inlet neck of the furnace. This gives greater combustion stability.
The inlet neck of the furnace should be 1.2-2 times larger in diameter than the diameter of the burner pipe.
If the diameters are still equal, then the cut of the socket should not reach the cut of the stove neck by approx. 1 cm. But in any case, you should first experimentally determine the position of the burner in which the most stable combustion of the torch is achieved, and only then think about mounting. All burner parts are made from standard components, so it won’t cost you much. I have stainless steel pipes, you can use regular water pipes. Transitions cast iron. Standard plugs from a plumbing store. I decided to adjust the air supply in this way. Simply turn the plug, which acts as a flap.
It should be noted that it is easier to light the burner in a different way than I did with manual ones. First, we enrich the mixture by turning the plug until the through holes are closed. Then we set it on fire. Then you can open the holes slightly. This is clearly visible in the video. Subsequently, the plug can be removed altogether. The selected nozzle hole diameter is about 0.5 mm. Approximate thermal power at gas pressure 2 kg/cm2 - 5 kW.
This 3/4″ burner is similar to the previous one. The difference is in size and, accordingly, in power. The selected nozzle hole diameter is about 0.8 mm. Approximate power at gas pressure 2 kg/cm2 - 9 kW. In all burners, power depends on the amount of gas leaving the nozzle, and this in turn depends on the diameter of the nozzle and the gas pressure. Only the efficiency of burning this gas depends on the geometry of the burner itself. I changed my mind about drilling the large burner plug. I want to pair it with a blower later
Please note that sealing the connections is necessary when supplying gas to the nozzle. The remaining connections do not need to be sealed.
On both direct burners, the nozzle manufacturing is somewhat different from the previous ones. A tube plugged at one end is inserted across a large pipe and grabbed. And only then a hole is drilled into the machine. This ensures alignment of the nozzle hole and the pipe. The video shows how to ignite the burner, having previously enriched the mixture by closing the damper.
How to make a burner for a gas forge
In addition to general instructions on how to make a forge, there are rules for installing a gas burner. A gas forge burner can be purchased at a store, or you can make it yourself.
You need to make a gas forge burner yourself, taking into account the requirements for it:
- ignition of gas should be completely safe;
- combustion must be stable;
- resistance to humidity inside the furnace;
- safety in case of changes in thrust and the risk of explosion of a flammable substance.
The burner is installed through a pre-prepared lining hole. The mouth of the burner is attached to a confuser, which is pulled through a steel gasket. Then pipes for supplying gas and air are installed.
Gas is supplied to the burner from a cylinder or network under the control of regulators. A test run of gas is carried out to check the regulators and pressure, and monitor the smell.
Manufacturing Features
The design features are that it is very easy to operate; there are no traces of soot or repulsive odors when using the gas burner. This device is compact and can be used virtually anywhere. The main component of the burner is the industrial valve. You can purchase a new part, however, and used ones that are in working order are quite suitable. The process of making a burner with your own hands begins with the handle, then the body and nozzle are made.
In order to obtain a burner that is safe to operate and does not waste fuel, you need to make it a rule to avoid scaling and adjusting the example circuits.
To be fair, it is worth noting that not all gas appliances are calculated according to the laws of gas dynamics. But if the manufacturer changes the dimensions of the design parts, then the Reynolds number of the fuel (or intake air) will go beyond the limits indicated in the original product. The burner with such “improvisation”, if we give an optimistic forecast, will begin to smoke and will be “gluttonous”, or even be completely dangerous in operation.
And one more important note regarding the manufacturing features of the burners: it is impossible to increase its power above 10 kW. And that's why
With a burner efficiency of 95% (which is an excellent indicator for an amateur invention), with a device power of 1 kW, it will take 50 W to self-heat. It is theoretically possible to get burned on the structure, but it is not fraught with explosion. But if you build a burner with a capacity of 20 kW, 1 kW will be superfluous. Threshold manifestation is expressed by the structure being hot or bursting into flames. Therefore, those burner drawings that are oriented at 7-8 kW should not be considered.