In the modern world, it is customary to bring back long-forgotten old things from the depths of history, and now the wooden bicycle is confidently coming into fashion. Of course, manufacturers do not offer it in the primitive form that it was hundreds of years ago, and you won’t have to walk your feet on the asphalt; on the contrary, these are quite solid premium models. The price of such newfangled products can be thousands and tens of thousands of dollars, which may not be affordable for the average person, so many people think about the question: how to make a wooden bicycle with your own hands?
Wooden bicycle
Accent on wood
Wooden bikes are distinguished not only by their unique attractive design, but also by their practicality due to the properties of wood:
- material strength;
- elasticity;
- ease of processing;
- vibration absorption, resulting in smooth running.
Manufacturers often use layering technology to create a flexible molded form that creates a solid frame, which adds strength. And they also often combine wood with carbon fiber to ensure the lightness of the product. The finished frame is treated with impregnations against moisture and decay, which ensures the product’s resistance to environmental influences.
The most common tree species used in production: ash, maple, birch, beech, oak, cedar, walnut, sandalwood and other varieties of mahogany. Another material worthy of attention is bamboo. It is, of course, not a tree, but it is not inferior in strength.
With electric motor
An electric bicycle is another type of three-wheeler for adults. It differs from others in the presence of a small electric motor, which allows you to move without physical effort. A very attractive option for people with disabilities. Perhaps this is the most popular modification of the “adult” tricycle in European countries.
Ease of operation, safety and reliability, decent speed (up to 20 km/h), the ability to transport up to 100 kg of cargo - these are not all the advantages of an electric bicycle. It will not take up much storage space. Moreover, folding bicycle models with electric motors have also been developed.
The only concern will be charging the batteries. This can be done from a regular 220 V outlet. The batteries are completely sealed and packed in a special removable bag for convenient recharging. It is enough for 35-40 km. Lead batteries need to be changed once every 4 years, gel batteries can last up to 10 years.
The disadvantages of an electric bicycle include the rather large weight of the batteries. But recent developments with lithium batteries show that electric motors have a great future.
Materials and tools:
- Plywood sheet 15 mm - 1 pc.
- Plywood sheet 20 mm - 1 pc.
- Wooden beam - 1 pc.
- Round beam 20×360 mm - 1 pc.
- Bolt M10x15 mm - 1 pc.
- Wheels 12″ - 2 pcs.
- Liquid polyurethane - 1 pc.
- Brush - 1 pc.
- Screws
- Bolt + washer + nut
- Screwdriver or electric drill - 1 pc.
- Jigsaw - 1 pc.
- Flat needle file - 1 pc.
- Emery block - 1 pc.
- Phillips screwdriver - 1 pc.
- Wood glue - 1 pc.
Step 1: Cut out all the parts from plywood. In the photo, the bicycle parts are laid out on an “inch” (each large square corresponds to a square inch - 25.4 mm x 25.4 mm) to represent the scale of the product. We transfer this photo by projection onto a sheet of paper or directly onto a sheet of plywood. The parts are cut out with a jigsaw from 15 mm thick plywood. All irregularities and splinters are removed with a file and finally treated with sandpaper.
Do not forget to use a groove cutter to cut out the longitudinal cutouts on which the wheels will be attached (on the sidewalls of the steering fork and on the back of the sidewalls of the frame), as well as holes at the upper ends of the sidewalls of the steering fork with a diameter of 20 mm.
Step 2: Assembling the steering fork and frame elements.
The sides of our bicycle should be located at an acute angle of 11 degrees and the apex of this angle is the steering fork.
We cut out a wedge-shaped blank (angle 11 degrees) from a solid wooden beam; it should be either the same in height as the width of the sidewalls or slightly less.
Then install the side parts of the bicycle frame on the side surfaces of the wedge using glue:
After the glue has dried, drill through holes at the top and secure the connection with bolts.
Tip: Since all operations are carried out at an angle, it is necessary to ensure reliable fixation of the parts using clamps. Also, before tightening the nuts, it is necessary to make small corner recesses for the washers using a Forstner cutter to prevent damage to the wood when screeding.
Finally, drill a through hole at the top of the wedge, into which we will insert the steering fork axle.
To attach the steering fork axis, we cut out rectangular parts from 20 mm plywood, corresponding in width to the side elements of the steering fork. In the center of both parts we will drill through holes for the steering fork axis. Assemble the steering fork. First put a washer on the bolt, then the first rectangle, then another washer, then the side frame elements fastened into the corner, then the washer, then the second rectangle of plywood, then the washer, then the nut and the second locking nut.
We attach the sides of the steering fork to rotating rectangles using glue and screws, as shown in the photo. For better fixation when the glue dries, use clamps. Insert the steering wheel into the large holes in the sidewalls of the steering fork and secure the connection with glue.
Step 3: Making the saddle.
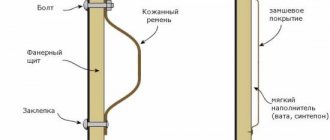
The saddle is a platform made of 15 mm plywood with an L-shaped holder.
The saddle is installed between two block spacers with a 5.5 degree bevel on one side. Adjust the height and secure the connections with screws.
Step 4: Finalization and testing.
Cover the wooden surface with waterproof varnish or liquid polyurethane.
Install the wheels with their axles into the pre-cut grooves on the back of the frame and steering fork and tighten with nuts.
The bicycle for your child is ready!
Compact sauna with mini pool!
WE ARE CONSTRUCTING A CAPITAL CELLAR!
A universal table for home carpentry!
How to make a stylish small sofa with your own hands.
What can be made from the remains of a car!
Reclining
A separate category of tricycles that are used as racing bicycles. This design allows you to ride in a reclining position or lying on your back.
The specific appearance attracts attention. This “adult” tricycle develops greater speed than standard models
Semi-recumbent bicycles are divided into:
- according to the intended purpose (sports, recreational and record racing);
— by the nature of the drive (with rear-wheel drive, with front-wheel drive and a movable carriage, with front-wheel drive and a fixed carriage);
- by wheelbase size (short, medium, long);
- according to the height of the seat above the ground: with a high, medium (to the ground 40 cm) and low (15-20 cm) seating position.
— semi-recumbent three-wheelers can be single or double (tandem).
How everything works
“I spent about a month searching for the right tree. Initially I cut 200×200 from timber. In the end I chose pine because I wanted to make a cheap bike. Plus, it is quite massive, has enough strength, and its softness gives the bike ergonomics. Everyone who switches from a regular bike to mine says that it is much softer and smoother,” says Gleb.
The guy uses Ukrainian wood, but orders all the components from Europe.
“My second test bike had cheaper components. But the longer I worked on the model, the more beautiful it became, and I simply didn’t dare put cheap rims or a saddle on it. The rims are now French, the tires and rear hub are German, the Brooks saddle is English. We don’t even have these components freely available; everything has to be ordered from Europe.”
When the guy found the materials and components, the search began for a workshop equipped with everything necessary.
“I needed a master who had a CNC milling machine for 3D milling, but it turned out to be difficult. But fate brought me to this, I think, not by chance. Andrey was also passionate about the idea of making a bicycle, and besides, he has an engineering education.”
Gleb was really lucky with the master - he not only took up milling, but also helped the guy master modeling, suggested good programs in which this can be done:
“Andrey does milling. I buy the material, cut and glue the blanks, then sand and trim. I have a small workshop. From the milled parts to the finished bike, it takes six days of work.”
The guy says that he read a lot about wood processing and tried different ways to achieve maximum strength:
“Even if the tree is not initially super strong, this can be achieved by gluing the parts together. The boards are glued together in steps.”
Gleb's bicycle weighs 17 kilograms and costs $1,200. It has two gears - thanks to a planetary hub with automatic shifting. Brake - foot brake. There are metal pipes under the saddle and inside the steering frame. Oak is used in areas of maximum load (carriage, steering wheel).
Best articles: Review of programs for cyclists for Android
The top of the bike is covered with water-repellent Dutch oil, which preserves the wood, protects it from moisture, but is almost invisible. If you smell a bike, it smells like wood, not chemicals. It can be washed, exposed to rain:
“This is a touring bike, it’s not designed for you to jump up three steps or go as fast as possible down a mountain. Yes, this is a little old school model – shape, color. But the new models will be more modern, with brighter colors.”
Interesting information
Below are some interesting facts related to the history of the development of two-wheeled units without motors:
- A bicycle without pedals was invented back in 1814, made of wood, and you could move around on it by pushing off the ground with your feet.
- The first bicycle race was held in the suburbs of Paris (the distance was 2 kilometers, 1868).
- In Russia, models with chain drive began to appear en masse in 1880.
- A significant breakthrough in the development of bicycles occurred in 1884. Scottish veterinarian Dunlop came up with a pneumatic splint. Initially, he tried to fill it with water, but this significantly reduced the speed. Then the inventor blew air into it and came up with a special valve that prevented the mixture from escaping back.
- China is considered the main modern bicycle manufacturer, since the majority of production facilities are located there (about 95% of production).
Improvement
A designer from Germany, Drez, created an ancient bicycle in 1817, which in fact was a wooden scooter equipped with a saddle and handlebars. The invention was named “trolley” in honor of its creator. This term is still used in relation to some self-propelled vehicles.
In the forties of the nineteenth century, the device was modernized, thanks to the efforts of Kirk Patrick Macmillan (blacksmith of Scottish blood). The former bicycle without pedals is equipped with metal rods fixed to the rear wheel. With the help of them it was possible to set the car in motion using the legs. The driver himself was located between the front and rear wheels, adjusting the direction using the steering wheel interacting with the front rim.
It is worth noting that engineer Thompson soon provided inflatable tires, which at that time did not gain popularity due to their technical imperfections. Mass production of bicycles with pedals and tubes began after 1867.
Improving the wheel design
For several thousand years, the history of the wheel made almost no progress in its development. And only in the middle of the 18th century, a new improvement finally appeared - tires were invented. The first wheel tires were made of thick fabric (canvas) and only then they began to be made of rubber.
One of the impetuses for further improvement was the invention in 1817 by the German professor K. von Dres of the first bicycle, more similar to a wooden two-wheeled scooter (it was called a “trolley”).
The appearance and improvement of the wheel is the most epic invention that pushed humanity to the beginning of the transport revolution, which in the 19th century included railway transport (the structure of which is also based on the use of wheels) and river transport - with the discovery of the steam engine, the first wheeled river steamers were launched.
The next step in history was the creation of cars, and already here the wheel structure has undergone a lot of improvements, which continue to this day.
Historical roots of the wooden bicycle
The first bicycles made of wood only vaguely resembled the modern design - the wheels were attached to a straight frame, and handles for control were attached to the front. There were no pedals or drive; the bicycle was driven by pushing the feet off the ground. In general, the design was more like a balance bike.
The first painting of a two-wheeled structure was painted by the artist Giacomo Caprotti, a student of the legendary Leonardo da Vinci, at the end of the 15th century. That is, we can safely assume that the history of the bicycle goes back at least half a millennium.
Something vaguely similar to a bicycle originated in the Renaissance
The Chinese, however, do not agree with this - according to their version, bicycles were invented before our era. To be more precise, using the drawings they found from 2,500 years ago, they managed to reproduce a real miracle of antiquity - a wooden bicycle booth.
The device is no simpler than a modern bike - that’s what the designers of that time tried
But let's get back to the balance bike. Officially, the inventor of the first bicycle is Karl von Dres, a German design engineer.
The invention dates back to 1818. Starting from the 19th century, the bicycle received a significant impetus in development: its design was modified several times, and at the end of the century, machines similar to the current ones began to appear.
Balance bikes with wooden frames are still made today
The wooden balance bike is not gone forever - modernity brings back retro from the distant past, giving a second wind. For example, bicycle scooters are no longer the same as they were in the 19th century, but are also made of wood. However, not only balance bikes are made of wood. These are quite ordinary, at first glance, large. Of course, such models are not common and often exist in a single copy.
From origins to modern times
Excluding dubious information about frescoes found during excavations with images of structures resembling a bicycle, as well as about the drawings and drawings of Leonardo da Vinci, the German baron Karl von Draize is officially considered the creator of this vehicle. The bicycle he made from ash was devoid of pedals and other mechanisms familiar to us today; it was set in motion by pushing off the ground with our feet, which is why it was called a “running machine”, and in common parlance a trolley. Despite the primitiveness of the design, this wooden bicycle marked the beginning of its further modifications and is the progenitor of all modern bicycles.
Today, the production of structures made from natural materials is rapidly gaining momentum in the sports industry. Many leading manufacturers can boast of interesting conceptual models. One of the most striking representatives of this species is the wooden electric bike. The symbiosis of good old wood and improved mechanisms is increasingly fueling the interest of bicycle modern lovers.
Folk craftsmen are not far behind in their creativity; some of them even manage to recreate a chain mechanism using only wood.
Sometimes funny, sometimes admiring designs delight with their originality, awakening the desire to make a bicycle out of wood with your own hands.
Standard velomobile option
Velomobiles, like other types of entertainment and sports transport, can be different in their structure and capabilities. But, despite this, there is still a standard for the external and functional content of this type of transport.
A velomobile, in its usual form, includes:
- A three-wheel design in which the front wheel is slightly larger than the two rear wheels;
- Steering wheel;
- Front frame;
- Connecting elements;
- Sitting.
Naturally, standardity is an opportunity to add color and add notes. After all, if a person converting an ordinary bicycle into a velomobile has taken on such an interesting mission, it means that his imagination is sufficiently developed and will help him make a special design.
A velomobile is not only a means of transportation and a way to pass the time profitably, it is also an opportunity to stand out from the crowd and show that the owner of the vehicle is special. Thanks to creative and unusual solutions, be it decor or a structural part of a velomobile, every craftsman can make the fruit of his efforts especially interesting.
Golden time
The heyday in the development of two-wheeled vehicles without a motor is considered to be the 90s of the nineteenth century. This is due to the advent of the pedal brake, as well as a free-wheeling device, which made it possible not to pedal unnecessarily. A handbrake soon appeared, but its widespread use began a little later.
The first folding bicycle was made in 1878, and in the next decade aluminum structures were invented. A vehicle with pedals, which could be used in a recumbent or reclining position, was invented in 1895. This modification was called “ricambent”. Its mass production began a few years after the presentation.
Penny farthings
The year 1969 is famous for the appearance of new bicycle designs. These bicycles were called penny farthings or spider bicycles. They looked like coins of different diameters: a penny was a large coin, a farthing was a small coin. The large wheel gave the structure stability and stability. The penny farthing was invented by Eugene Meillet. Spider bicycles were made with spokes, which reduced the weight of the wheel and improved balance. Only men could ride penny farthings, because you had to climb on them from behind, standing on a step, and ride it with your legs stretched out in different directions, which is impossible to do in a skirt.
The time when spider bicycles were invented was the time when such devices were popularized. Following the advent of penny farthings, bicycles for women are invented. They had 3 wheels, which is why they were called tricycles. Instead of one big wheel, they had two. The saddle was between the wheels. A chain drive was introduced on tricycles, which improved the quality of their movement.
Tandem bicycles also appeared, in which a man sat behind a woman. They organized collective trips out of town. A man and a woman were spinning wheels together, sitting next to each other. Penny farthings reached speeds of up to 25 km per hour, so they became popular among students, fashionable youth and men of all ages. The large wheel made the structure more stable.
But these devices were dangerous because when turning, the center of gravity shifted and the large wheels tilted to the side. Sometimes they turned over, dragging the would-be cyclist along with them. The rear wheel was useless when braking. The brake was on the steering wheel and excessive pressure on it caused the person sitting to fly over the steering wheel, getting their feet tangled in it. But regardless of the health threat, penny farthings remained popular for a long time. There was a need to improve the bicycle to make it safer.
Further development
The bicycle got its name thanks to Pierre Michaud, who patented a pedal drive mounted on the front wheel. At the end of the 19th century, the “penny-farthing” model became popular, so named because of the analogy between the diameters of the coins (a penny is smaller than a farthing). The pedals were mounted on the large front wheel. The saddle was located on top of them. Since such a vehicle had a displaced center of gravity, a bicycle with a large front wheel was considered a rather dangerous modification, riding which required the attention and balance of the rider.
An alternative to this device was three-wheeled models, which quickly gained popularity. The next stage in the development of the bicycle can be considered the use of a metal wheel with internal spokes. A similar invention was proposed in 1867 by Eduard Cowper. Literally a couple of years later, the vehicle was equipped with a frame, and in the late 70s a chain drive appeared (the inventor was the Englishman Lawson).
The emergence of pneumatic tires
Pneumatic bicycle tires were created by an ordinary veterinarian, John Boyd Dunlop. He treated animals in small villages. But Dunlop was an inventor by vocation. In 1888 he invented pneumatic bicycle tires. The roads in the 19th century were full of holes and potholes, so it was impossible to drive along them without grinding and shaking. Wheels were then made of bare metal or covered with thin rubber. John's son loved to ride a bicycle and his father watched with alarm as his bicycle vibrated and shook on the rough road.
John Boyd Dunlop measured the diameter of the wheels, took a water hose, cut it to length and wrapped the wheels. To achieve at least some kind of tightness, he covered the joints with a thick tarpaulin. To avoid slipping, I put rubber on the tarpaulin. Then he pumped air into the wheels. He first made pneumatic tires for his son's tricycle, and then for an adult model. Soon he received a patent for their creation.
Best articles: How to ride a bike without hands
Late 19th century
The penny-farthing and similar models were replaced by a bicycle that vaguely resembles modern modifications. It was made by English craftsman John Kemp Starley in 1884. The car was called “Wanderer” (Rover). After 12 months, mass production of this version began. The unit had a chain drive, the same diameter wheels, the driver's seat was placed in the middle, between the front and rear rims. Subsequently, the Rover company began producing cars and other equipment until 2005, after which it went bankrupt.
In 1888, Scottish engineer John Boyd Dunlop proposed rubber tires that were softer and more comfortable. Reliable cameras compared to rubber counterparts quickly gained popularity. If the old bicycle was compared to a “shaker” for bones, now the ride has become much smoother and more comfortable.
Modern models on wooden frames
A bicycle is an environmentally friendly and quiet transport. It does not pollute the environment with exhaust, does not irritate with crackling and noise, and is also less dangerous than a car. Perfect. But it turns out that you can make a bicycle even more environmentally friendly - assemble it on a wooden frame.
Indeed, with wood, the bicycle becomes almost 100% natural - the production of metal alloys and carbon fiber, which is unsafe for health, is completely eliminated, and besides, wood is a more affordable material. Tireless designers managed to make wooden bicycles a reality. Let's evaluate the five best models:
1. Perfect Day - a mountain bike with a wooden frame - is perhaps the most durable among its metal counterparts. The idea of creation and the exclusive model belongs to the Dvoika company. Frame material – birch.
In general, this is a full-fledged MTB, in the quality we are used to seeing it: frame geometry, multi-speed transmission, powerful shock absorption, steering wheel design, disc brakes, aggressive tires.
2. Ash-bike - a unique solution by Dutch designer Paul Trimmer. The lightweight and environmentally friendly bicycle is made from solid ash boards.
By design, this model occupies an intermediate position between three classes of bicycles: road, highway and mountain. From the road bike, the ash bike took a single-speed transmission and the type of wheels, from the road bike - lightness (about 10 kg) and the relative position of the steering wheel and saddle, from the mountain bike this model adopted the shape of the steering wheel and disc brakes. Indeed, v-brake is inappropriate here - you would have to cut the wood, and this is already ugly.
3. Aero – a stylish model with an “eye” frame. Unlike previous models, this one is equipped with a thin metal and rigid fork. The rear seatstays seem to merge with the front of the frame, there is no seat tube - the saddle is simply attached to the top of the “eye”.
The model belongs to the Ukrainian designer Maria Koroleva. The emphasis was on originality and style, while the bike itself belongs exclusively to the pleasure class. However, walks with such a bike will be remembered forever!
4. Bough Bike – an electric bicycle made of wood with a two-speed belt transmission. The engine power is 225 W, the maximum acceleration speed is up to 25-30 km/h without the cyclist's power consumption. Brakes – manual rim and classic drum.
The frame material is oak wood from France, the wheel fastenings and the joints of the frame parts are made of stainless steel.
5. Guapa – urban singlespeed on a bamboo frame and rigid aluminum fork. The model is distinguished by its lightness and high directional stability on smooth roads.
The bike is perfect for fast city riding and will delight cycling enthusiasts and adherents of an eco-friendly lifestyle.
What changed at the beginning of the 20th century?
The ancient wooden bicycle of the early 20th century has long since sunk into oblivion. In 1915, models equipped with rear and front suspension appeared. Their main purpose is to be used for the needs of the Italian army. Ten years later, the device featured ball-type bearings, multi-speed bushings, a conveyor assembly method, a chain-drive speed controller, and steel pipes with foot brakes.
The first gear shift mechanisms were far from perfect. Special sprockets were mounted on the rear wheel on both sides. To change gears, it was necessary to stop the equipment, remove and turn over the wheel. In addition, it was necessary to adjust the position and tension of the chain.
How to make a bicycle out of wood
Some manufacturers offer the buyer a kind of “do-it-yourself” construction kit - that is, such a kit contains all the parts of the bicycle, as a result of which, as a result of fastening, a full-fledged vehicle is obtained. You can also find instructions for assembling branded bicycles posted on the websites by the developers themselves (not for free) and make a similar bike yourself. But if your craving for modernization is coupled with the desire to own an exclusive model, then you should still make a bicycle out of wood with your own hands.
So, you, inspired by the ideas of modern designers, have decided to update your old bike using a wooden frame or assemble a new one almost from scratch (for which, of course, you will have to buy additional parts if you don’t want to cut every gear out of wood).
Bike with wooden frame
Required materials and tools:
wood (it is important to choose the right material, the wood must be strong enough and so that the fasteners adhere well to it); wood glue; epoxy resin; carriage connecting the mechanism to the frame; plywood; wheels, handlebars and the rest of the mechanism of a regular bicycle; plane; screwdriver or drill; hacksaw; bolts, screws.
You need to start by creating a sketch of the bicycle frame design on paper. As an alternative, you can simply find a suitable sketch on the Internet and print it in the desired format
When designing a frame, it is important to take into account the dimensions of the remaining elements of your bike. The design must fit adequately into the rest of the mechanism. When the paper and plywood model is ready, we begin to make the bicycle frame by gluing thin layers of wood together. Cut the boards according to the template and process them with a plane, paying special attention to the corners. Glue all layers (there can be several of them, if desired).
After all the procedures, two wooden parts of the frame remain, which should be given their final shape and inserted inside (immediately gluing the surfaces), metal tubes cut exactly to the size of the wooden part. It is desirable that the tubes have as many slots as possible so that the finished product is lighter in weight
Press both halves of the frame until they are completely set; you can put them under the press for a while. The forks are made from several wooden strips glued together using plywood and bolts, and attached to the main part in the same way. Sand the finished frame and coat it with varnish. Assemble the remaining parts of the bicycle together, check each mount for strength.
Now your exclusive beauty is just waiting for a test drive, ready to amaze with its originality and attract attention. Perhaps in the future such models will not be uncommon on the roads, but for now such non-standard solutions surprise and fascinate the public
If you're a jack of all trades and love creating cool things, why not learn how to make homemade bicycles. You can ride around the city on a bicycle, show off your unusual homemade structure to your neighbors, and most importantly, show your son what talents his father has, teach him basic techniques and further strengthen the concept of “master” in the house.
How to make a headlight for a bicycle yourself? How to choose a suitable LED for a flashlight? Parts you will need, how to assemble and attach to the bike.
How to choose a battery for an electric bicycle. What characteristics do different types of batteries have? How to assemble a battery with your own hands.
Which hypothesis is correct
The official and now recognized version of the origin of the wheel considers its homeland to be Mesopotamia or Mesopotamia, which is argued by scientists by the appearance by that time of tools that could not be dispensed with in the manufacture of wheels.
The same hypothesis is presented in schools and other educational institutions; many films and cartoons have been made that tell the story of the wheel for children, its development, improvement and the emergence of new types of transport.
It would be appropriate to mention the philosophical meaning of the wheel “Movement... life... infinity”, which confirms the essence of its discovery.
How to make a bicycle trailer out of wood
A wooden trailer is best suited for children's bicycles. It does not withstand heavy loads, but 20 kg is enough for transporting small loads.
Materials required for manufacturing
- Two wheels (10 inches),
- Plywood panel (4x4ft),
- Thin board and plastic,
- 2x4 boards (8 feet long),
- Glue,
- Putty,
- Paint in several colors
- Square steel pipe,
- PVC pipe,
- Fastening tools,
- Drill,
- A circular saw
- Screwdriver,
- Other working tools and small accessories.
Side panels and floor
The side panels of the bicycle trailer and the bottom are cut from sheets of plywood. The walls should have a semicircular shape. The floor panel is 15 inches wide and the same length as the side panels (31 inches).
Best articles: History of the creation of the first bicycles
After cutting, all three parts are fastened with screws - the holes in them are drilled in advance, with a drill of a smaller diameter. The surface of the trailer base is primed with white paint.
Strengthening the Foundation
The mount will bear most of the load. If you assemble the “skeleton” correctly, the trailer will not be deformed. To secure the trailer, two long pieces of board (14 inches) are placed on the front panel, top and bottom. The same board is attached to the bottom on the opposite side. Two long boards on the sides complete the “skeleton”.
The boards are secured with three screws to the floor and side panel.
Roof
The trailer roof must be made of flexible material. Thin board, plastic panel, and (ideally) a large poster frame will do. The length of the roof panel is 14.75 x 36 inches. You need to cut it out with a sharp knife. After this, primer paint is applied to the panel and the roof is attached to the trailer. The corners of the frame are painted in the desired color. They are attached to the roof using self-tapping screws. Space each one 6-8 inches apart.
Wheels and axle
A mark is made on the bottom of the trailer: where the axle will be placed. Cut two 15-inch lengths of plywood. One is divided in half (about 2.5 inches wide). The smaller pieces are attached to the bottom of the trailer using screws on both sides of the axle. A piece of greater width is attached to the top. A piece of PVC pipe will be used as pads between the wheel bearings and the body. The wheels are held on the axle using clamps.
Door and other elements
A hole for the door is cut in the trailer roof. Leave 2-inch holes on the sides. From the remaining piece you need to make a front bumper. It is held on the roof with glue. While the glue dries, it is strengthened with adhesive tape. When the bumper is dry, a coat of paint is applied to it.
The door is made of a piece of plastic. The panel is cut to the required length and width and attached to the roof with screws. After this, the door is painted with the same paint as the trailer.
Additional decor
You can further decorate the trailer: paint the bottom part with the same paint as the corners and bumper. This is easy to do using strips of duct tape. The trailer door will be closed using a latch strap. On one side it is held in place with a screw, on the other there is a hook that is attached to the screw.
You can also add lighting. A 7 amp battery, a wire with a fuse, and all wires are located under the door of the trailer.
Fastening
In order for the trailer to be a trailer - to follow the vehicle - a piece of steel pipe is mounted to it (attached with self-tapping screws to the brackets). A spring axle is attached to the pipe.
The trailer is ready to go on a long journey with your bike.
The first carts
The history of the creation of the wheel is directly related to the advent of agriculture, because the fertile land in the river valleys of Asia, Egypt and China had to be cultivated. The appearance of such inventions as the plow and sail also dates back to this time.
At first, people began to make two-wheeled carts, when 2 wooden wheels were mounted on an axle. The very first wheels were made from solid logs. Ancient people cut a circle from a log or fastened it from boards, cutting it in a circle.
The carts moved with the help of harnessed animals (donkeys or bulls), but such a cart could only be turned by hand. Later, four-wheeled ones also appeared (around 3500 BC). Of course, such designs were not invented in one year; improvement continued for centuries.
Cave paintings found by archaeologists show carts with a very primitive design: four wheels mounted on axles, and a platform on top to place the load. Such ancient devices were discovered in Mesopotamia, the seat of civilization where the development of metalworking first began.
The spread of wheeled structures occurred in Europe and northern Asia; it is not for nothing that the word “cart” is of Mongolian origin. Images of carts were found in Southern Siberia (mid-2 thousand BC). Nomads even began to make houses on wheels - large carts with a roof. Gradually, such structures reached China.
The next improvement related to the wheel was a design in which the front wheels could turn freely using a swivel front axle. Now people, sitting in the cart, could turn it, controlling the animals.
At the same time, there was a need to build roads so that vehicles could move first between the field and the settlement, and then between settlements they began to transport food and cargo.
The fate of the inventor Drez
Karl Dres was born on April 29, 1785 in Germany in the city of Karlsruhe. Graduated from Heidelberg University. In 1811 he became a forester. But after a while he had a desire to invent something. For the first time he invented a machine that drew musical notes. The invention gained popularity because drawing lines is a tedious and difficult task.
The second he created was a four-wheeled bicycle. It was driven by muscle power. But at the Congress of Vienna it was heavily criticized. Critics pointed out to him that a four-wheeled car is difficult to push, moves slowly and is subject to shaking. But Drez was a man who never lost heart and always believed in his strength and his mind. Karl corrected all the critics' comments. Instead of 4 wheels, he made 2 and added a steering wheel. This is how the first wooden bicycle appeared. For it he received a royal prize.
To promote his invention, the baron went to travel around the world. For 5 years he showed what his design was capable of, attracting more and more bicycle connoisseurs. But trouble happened: my father fell seriously ill. Karl had to return home. The last minutes of his life, the father felt that his son loved him and was next to him. He managed to see his son's next invention - a typewriter. After his father's death, his enemies began litigation over property.
In 1937, Drez suffered a stroke. After recovery, he moves to a hut in the forest and continues to do what he loves: inventing. He places the bicycle on the iron rails. So the word trolley received its new meaning, and the new device was used in practice for a long time. Drez's other inventions were a 16-key typewriter and a meat grinder. The typewriter was the ancestor of Morse code.
In 1849, Karl von Dres supported the revolution. He renounced the title of nobility and began to call himself a citizen. The revolution was soon suppressed. The inventor was declared crazy. His property was taken away and his pension was deprived. So Karl Dres became a beggar. He died on December 10, 1851 in his hometown.
Using the wheel in other devices
Gradually, the wheel began to be used in other devices. Over time, it found its use for water devices, according to the records of the scientist Vitruvius already in the 1st century. BC e. Water wheels also spread to ancient Rome. Two types of such wheels were used: gravy (for slow-flowing rivers) and bulk (on fast mountain rivers).
During construction, people also began to use a lifting block, the basis of which is also a wheel. Later, the wheel found another application - a spinning wheel was created for spinning wool. According to historical data, it was invented around 1 thousand BC. e. in India and surrounding areas of Asia.