| How to replace heat shrink | Description |
| Insulating tape | The most obvious option for replacement. It is applied by wrapping it around the desired area. It has almost all the same properties as heat shrink. However, over time it begins to peel off, spoiling the appearance of the isolated area. |
| Polymer tubes | Any tubes are suitable, for example from a dropper or a hydraulic level. They just need to be placed over the exposed wires. The tubes can be preheated to make them easier to use. |
| Thread/cord | Wrap the wire with thread or cord and glue it. This is not the most effective analogue, and the process of such isolation takes a lot of time. |
| Rubber tube | Any rubber nipple tube of suitable diameter is suitable. It, just like polymer tubes, needs to be pulled over the bare wire. For a tighter fixation, the tube can be heated with a lighter. |
| Heat shrink sleeves | These sleeves are used for welding with optical fiber. Place the sleeve over the wire, connect the ends, drag the sleeve to the place where the wires are fixed and heat it with a lighter or burner. After a few minutes of cooling, you will have reliable insulation. |
Heat shrink is the most popular and reliable means for insulating wires. The principle of its use is as simple as possible. Despite its apparent simplicity, heat shrinkage provides good results. In some cases, you have to look for something to replace the heat shrink because it was not at hand.
There are several analogues, however, you need to take into account that they do not provide the same result as the original.
How to insulate wires with heat shrink: let's look at the details
The very name of this material contains the word “temperature”, which will help give the coating the required level of strength. To do this, the heat-shrinkable tube is preheated to +120C degrees.
This is done to give the material greater elasticity. Immediately after heating, the sealed coating can be applied to the desired surface.
As the tube cools, it will return to its original shape. The described technology is convenient in another way. For example, the insulation of a wire with two exposed ends is done without any seams. As the tube cools, it literally “tightly” solders both parts.
The key to success lies in a properly selected heating tool so that it does not “glue” the wire to the wall:
- Heat guns;
- When using a gas burner, make sure that the flame is yellow;
- Construction hair dryer with attachments;
- Lighter;
- Matches;
- Boiling water.
The last three listed methods are suitable for cases where heating is done by hand. In general, a simple procedure allows you to insulate exposed wires with heat shrink. The main thing is to choose the right temperature and prolonged thermal exposure.
Do-it-yourself thermotube
Heat shrink tubing is an innovative insulation method that is used when working with electricity.
This material is much preferable to traditional electrical tape, as it creates a uniform, absolutely sealed electrical insulating layer.
To the question of how to heat a heat-shrinkable tube at home, we will try to give a detailed, constructive answer.
Main characteristics
Heat-shrinkable tubing is a special insulating element that, when heated, changes its diameter, indicated in millimeters (mm), reliably protects and insulates the base placed inside from damage.
Heat-shrinkable tubes are made from heat-polymer materials with high heat-resistant properties.
There are certain requirements that apply to heat shrink elements:
- elasticity;
- resistance to high temperatures;
- lack of flammability;
- resistance to aggressive environments;
- rapid deformation;
- tensile strength – 15 MPa and above;
- elasticity – the ability to increase by 300% of the original size.
The most popular insulator are tubes that can deform at temperatures from 55 to 120 degrees Celsius, but there are products that can withstand heating up to +300 C.
The properties of this thermal insulation allow, when heated, to completely follow the contours of the object that should be insulated.
Basically, thermal insulating elements are used for electrical insulation of contacts, wires, terminals, but in some cases this material is used to protect metal products from corrosion.
Application area:
- electricity;
- cable production;
- protection of equipment used in electrical installation work;
- installation, repair of couplings;
- marking of wiring during insulation through the use of elements of different colors;
- in nuclear energy as a supplement during installation work.
In addition, it is used to protect wires from destruction and insulate objects in all areas of production.
Open flame shrinkage - pros and cons
An open flame is a lighter, candle, match or other source of fire. If we consider an open flame for heating, then it is worth knowing some nuances:
- Thermal insulation may undergo severe deformation when exposed to strong heating;
- If the flame is not removed in time, the heat shrink may simply burn out;
- White, colored heat-shrinkable element may smoke when heated.
The main problem with open fire shrinkage is that the source of heat is always at the bottom, and in order to heat the insulator evenly, the connection must be constantly rotated. This is the only way it will heat up evenly.
In addition, you must strictly maintain the distance from the structure to the open fire. It should not be less than 3-4 cm.
, it is at this distance from the flame that the temperature indicator is the highest.
Do not use gas burners or turbo lighters for heat shrink tube for heating - it will immediately become unusable.
Application of various methods for heating
There are several heating methods, each of which can provide high-quality heat treatment. But there are also some that are not recommended.
The most popular, at the same time controversial option is a lighter or matches .
This option can be used if there is no other source of high temperature at hand.
You can only shrink a small section of wire with a small cross-section using this method. This option is not suitable for large structures.
If we are talking about large products, then heating will take a lot of time, and the connection itself will turn out to be of poor quality.
And how many times will this procedure need to be repeated if it is necessary to process several areas with a large cross-section?
The same can be said about the lighter.
Some home craftsmen try to use a regular hair dryer for shrinking, which every housewife has.
But it is worth remembering that this device cannot provide the required temperature, so high-quality compression of the insulation will not work.
Important! Depending on the brand of material, the heating temperature is 90-150 degrees.
A household hair dryer produces a stream of hot air t 700 C at the outlet of the nozzle.
If you use a narrow nozzle, then of course it is possible to heat a small area with a small diameter; as for large sections, the hair dryer will simply fail, and the insulation will turn out to be of poor quality and unreliable. Do not forget that there are some heat shrink models that can be compressed at a heating temperature of 350 degrees.
The result of such work may be a loose fit of the material to the insulation site, into which moisture can easily penetrate, so it is worth using a special tool.
Heat Shrink Tools
In fact, there are only five heating construction tools. Let's look at them:
- construction high-temperature hair dryer for heat-shrinkable tube;
- special butane-based burners;
- gas soldering irons;
- propane burners;
- infrared device.
The best option for heating heat-shrinkable, thin-walled elements is a construction hair dryer . Its temperature conditions can be adjusted; in addition, you can purchase special nozzles for uniform heating.
Its disadvantage is that the heating of thick-walled material will take a long time, and the quality of compression will be unsatisfactory.
Before you start heating with a hairdryer, you need to hold the heating area with your hand so that the strong air flow from the nozzle does not cause the element to move from its place.
A burner with infrared radiation does not have these disadvantages, since heating is carried out in a matter of minutes, without a strong air flow.
Important! When using infrared radiation, you should know that elements of black or dark shades absorb heat faster, so there is a high probability of burning through the thermal insulation when heated.
Gas burners are good to use because the flame has several functions. It is worth understanding that shrinkage should be done on the softest flame.
How can you tell if the flame is soft? Adjust the burner so that all flames are yellow; the same indicators should be used when using a gas soldering iron.
Interesting to know! Since this thermal insulation is used everywhere, including in mechanical engineering, the question arises: how to heat the heat-shrinkable tube for a gas pipeline.
There is one most important limitation: open fire in any form cannot be used for heating.
It is better to use a hair dryer or an infrared emitter to insulate the gas pipeline.
A propane torch is the most suitable tool for compressing thick-walled thermal insulation elements.
- Thermal insulator size;
- Wall thickness;
- Material of manufacture.
Before choosing one heating method or another, study the characteristics of the material you plan to use.
Watch the video - how to use heat shrink, how to heat it, etc.
How is heat shrink better than electrical tape?
There are two main indicators for which thermal tubes are preferable to insulating tape:
- When using a thermal insulator, you don’t have to worry that it will lose its desired properties over time;
- the electrical tape sticks to the insulated surface and leaves a dirty mark on it. As for thermal tubes, with the correct selection of shade, you can get an aesthetic appearance of any product. Removing the material is not difficult: you just need to cut the heat-shrinkable tube lengthwise;
- a very convenient material, if the contacts are very close to each other and wrapping with electrical tape is problematic - there is not enough space.
Thanks to their positive qualities, thermal tubes have become so popular and are used in many fields of activity.
Watch the video
Types of tubes, how to choose according to characteristics
There are several types of heat-shrinkable tubes, differing in design and nature of operation:
- Adhesive heat-shrinkable tube – has an adhesive layer on the inside. This is a very popular material for insulation, since when heated, the joints are completely sealed. Thanks to this, the connection is reliable. The shrinkage coefficient of this tube is 300%, which allows you to isolate objects whose diameter is much smaller than the tube itself. The adhesive heat-shrink tube can be cut, if it is not possible to put it on the element entirely, and then heat it up; thanks to the inner layer, the seam is hermetically sealed.
- Thick-walled thermo-shrinkable tube - made from polyolefin. This is a very affordable insulator, it is easy to use, and such a tube costs much less than an adhesive tube. This thermal insulator has a very wide range of colors and can be divided into:
- without fire suppression;
- thermotubes with combustion suppression.
The second option is used as heat shrinkage in electrical engineering production, military industry, and explosive enterprises.
These heat pipes are capable of self-extinguishing if they are not exposed to constant open fire, since non-flammable substances are used in production.
- Special thermotubes are used in specialized enterprises for additional insulation. There are several subtypes of material:
- fluorescent - used in dimly lit rooms, these tubes absorb light energy during the day and begin to release it at night;
- high-voltage elements - used for insulation work, when installing high-voltage networks;
- Teflon - used in the chemical industry;
- corrugated - used for insulating tool handles and electrical appliances.
- Fabric Heat Shrink Tubing - Flame Retardant, Halogen Free, Braided Fiber. Used to prevent abrasion and mechanical damage to wires and plastic pipes. When heated, fabric insulation decreases in size by half, which allows you to insulate products of non-standard shape.
These are the most common types of heat-shrink insulation, which are used in all areas of production.
Watch the video - recommendations on heat shrinking, what to heat with, etc.
Which products are best to use and why?
Experts advise using polyolefin tubes. Why, out of the total number of heat-shrinkable tubes, is this one preferred?
The fact is that, thanks to the manufacturing material, these tubes received the following characteristics:
- resistance to chemical influences;
- incombustibility and fire resistance;
- tensile strength;
- good shrinkage.
This is a reliable product that is produced using the latest technology and according to the requirements of the production process. They are produced in any configuration and for various types of thermal insulation.
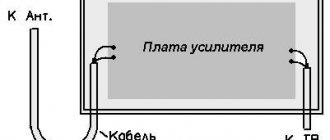
Protecting exposed wires
Having understood the basics, you can move on to the practical part of preserving electrical wiring from external influences. We are talking not only about water, but also about dampness, accidental damage and even pets.
It all starts with properly prepared two or more parts that need to be insulated with heat shrink.
All traces of dirt are removed from the surface of the wires. This is done using delicate cleaning products.
The further procedure is as follows:
- Electrical wires are degreased using a solvent;
- Wipe them gently with a soft cloth;
- If the electrical wiring is covered with PVC insulation, it must be removed using mild sandpaper;
- Using a lighter will help remove the polyethylene insulation materials.
Before starting work, you should clean the wires from traces of grease, dirt and the oldest insulation. This is done with a lighter or not very rough sandpaper. As soon as the wires are free of coating, you can begin to work.
Advantages and disadvantages of heat-shrinkable products
Heat shrink for wires has the following advantages:
- the ability to hermetically crimp products with complex relief surfaces, providing electrical insulation and mechanical protection;
- high strength with respect to tensile forces;
- abrasion resistance;
- chemical resistance to acids and alkalis;
- simple installation that does not require special skills or special tools;
- elasticity and ease of deformation during installation;
- resistance to open flame.
Note! The tube HERE reliably crimps wire connections, the diameters of which vary significantly. Thanks to tight crimping, the connected products do not move when exposed to mechanical factors, and the conductors themselves become more rigid and resistant to damage
Crimping HERE for conductors of different diameters
Among the shortcomings HERE, the following circumstances are noted:
- The thermotube is a disposable product. If it is necessary to remove it from the conductor, the polymer will have to be cut along the entire length of the fitting.
- The cost of heat-shrinkable tubes is higher compared to the price of traditional electrical tape.
- With increased abrasive loads during repeated contacts with foreign bodies, it is preferable to use several layers of electrical tape or corrugation (plastic or metal).
Secrets of choosing: heat-shrinkable tape
Experienced builders are familiar with the axiom that new heat-shrinkable tape should be smaller in diameter than the ends of the wires that need to be connected and insulated.
Most reference books even indicate an approximate ratio of 20%. From a practical point of view, this figure cannot be considered true in the last resort.
Connecting individual wires “in a twist” is not always possible with a 20% excess of the heat-shrink tube over the wire itself.
The following practical tips will help to simplify this manipulation a little:
- Heat-shrinkable tubes sold in the retail chain have a certain heat-shrinkage coefficient;
- At home, it is better to use material with a 2:1 ratio;
- The number on the left side indicates how much the tube will shrink in size after cooling;
- On sale you can find materials that insulate wires with a high ratio;
- First, they need to be tested in the field;
- A small piece of tube is heated to a temperature equal to 120C*1/2 = 60C degrees;
- Depending on how much weight has been lost, a decision is made as to whether it can be used in the future.
At the time of purchasing a connecting material, it is necessary to study its performance characteristics. In view is the shrinkage coefficient - an indicator that reflects the ability of a material to change its original size after heating and cooling. Isolating, for example, headphones can be done using a coating with a minimum ratio of 2:1.
We solve difficult questions: what can replace electrical tape?
This question comes up quite often, because traditional insulating tape is not always suitable. A heat-shrinkable tube with certain characteristics will help replace it. For example, it is necessary to connect and protect the wiring through which current flows. It is clear that plasticine is not the best sealant in such a situation, not to mention the fact that using tape is an equally stupid idea.
To work, you will need a thermal gun, the operating mode of which is set in the range from 120 to 200 degrees. Setting the mode to 70-120 degrees, instead of the one indicated above, is necessary when using Chinese-made tubes.
In the future, you need to adhere to the following algorithm:
- Heating always starts from the middle of the joint;
- As it warms up, the heat source is carried out in a circle, except for the corners;
- You need to make sure that the thermal sealant “presses” tightly to the central part of the wire;
- The point of the metal junction gradually heats up;
- After this, you need to gradually heat the two end parts so that after cooling they can quickly restore their original size;
- Give the joint about 2 hours necessary to cool;
- If you can write on the finished product with a washable marker without compromising the strength of the insulating coating, then the work has been done efficiently.
Heat pipes: installing a warm cable on heating pipes with your own hands, video instructions, photos
Heat pipes are heat transfer devices, the main feature of which is the ability to transfer large thermal powers with small temperature differences (gradients). Devices of this type are widely used in thermal power engineering, the chemical industry, electronics, and other areas of industry.
In this material we will try to highlight the principle of operation of heat pipes as clearly as possible, as well as talk about the scope of their application.
Glass body heat pipe
Operating principle
The operating principle of heat pipes is that energy transfer occurs through evaporation and further condensation of the liquid. To understand how this happens in practice, you need to imagine a closed container made of metal with good thermal conductivity and filled with a certain amount of water.
Heat transfer processes look like this:
- When one part of the container is heated, the water in it will turn into steam.
- Leaving the liquid, water vapor hits the cooled surface, as a result of which the steam again turns into a liquid state and flows down to its original place . In this case, a large amount of thermal energy is removed through the walls of the metal tank.
- The cooled water is heated again and the process is repeated..
This design is called a thermosyphon. Although it is not a heat pipe, the principle of operation is the same.
Note! The thermosyphon can only work as expected if its condensation zone is located above the evaporation zone. This ensures that the condensate returns to the heating site.
General information about pipes
However, heat pipes often mean not only devices for heat transfer, but also pipes that are used in thermal systems. Below we will talk about the types of these pipes, as well as the features of their use.
Pipes for heating networks can be made from a variety of materials.
The most common heat pipes include:
- Asbestos cement pressure pipes
- Bimetallic pipes
- Galvanized Carbon Steel Pipe
- Carbon steel pipes with enamel or glass-ceramic coating.
Note!
Not only the heat loss of the pipes during transportation of the coolant, but also the durability of the heating system itself depends on the material used.
That is why the choice of material for heating network pipes must be approached extremely responsibly.
Below we will look at all of the above types of pipes and analyze their advantages and disadvantages.